основные различия между поршневыми и запорными клапанами
Sep 26, 2024
On this page
Valves are critical components in industrial systems, designed to control fluid flow. Piston valves and globe valves are two common types, each valve with distinct characteristics in terms of operation, sealing performance, durability, and application scenarios. This article provides a detailed comparison of piston and globe valves, examining their structure, operating principles, applications, advantages, and disadvantages.
A piston valve consists of several key components, including the valve body, bonnet, stem, piston, handwheel, sealing rings, and a cage. Its core operating principle involves rotating the handwheel to drive the stem, which moves the piston up and down between two sealing rings, controlling the opening and closing of the valve.
Sealing Mechanism: Piston valves use an interference fit sealing method. When the piston inserts into the sealing rings, the rings are compressed, tightly gripping the piston. This radial force exceeds the fluid pressure, ensuring an effective seal. When closed, the piston fully inserts into the lower sealing ring, blocking fluid flow. When opened, the piston disengages from the lower sealing ring, allowing fluid to pass through the cage and the lower sealing ring to the outlet.
Material Advantages: The sealing rings are made from advanced non-metallic materials, which offer excellent resistance to high temperatures, high pressure, and corrosion. This ensures long-lasting elasticity and sealing effectiveness. The durability of the material also reduces wear between the piston and the sealing rings, extending the valve’s service life.
Piston Processing: The piston surface undergoes precision machining, resulting in a smooth surface that reduces friction and enhances sealing effectiveness and durability.

Strong Sealing Performance: The large sealing area and tight fit between the piston and the sealing rings ensure reliable sealing, especially under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions.
Good Durability: The wear-resistant properties of the sealing material, along with the large contact area between the piston and sealing rings, reduce wear during operation, resulting in a longer service life.
Adaptability to Harsh Environments: Piston valves can withstand high temperatures and high pressure, making them suitable for industries such as chemical processing, petroleum, and natural gas.
Slow Opening and Closing Speed: The piston moves slowly within the sealing rings, resulting in longer opening and closing times, making it more suitable for applications where speed is not a critical factor.
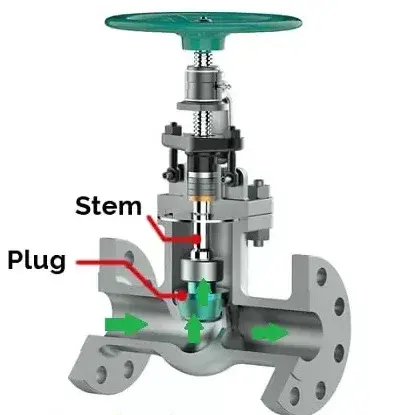
Globe valves are a type of forced-sealing valve that uses the linear motion of the stem to move the disc up and down along the direction of fluid flow, controlling the valve’s opening or closing. Its basic structure consists of the valve body, bonnet, stem, disc, and sealing packing.
Sealing Mechanism: The globe valve achieves sealing by applying pressure on the disc against the sealing surface. When the medium enters the valve from below the disc, the operator must overcome the pressure of the medium and the friction between the stem and the packing. To close, sufficient force must be applied to ensure the sealing surface is tightly sealed without leakage.
Fluid Control: Due to the relatively complex flow path within the valve, the fluid encounters significant resistance when passing through. This makes globe valves suitable for steady on-off operations but less ideal for frequent flow adjustments.
Simple Structure: Globe valves are relatively simple in design, making them easy to manufacture and maintain. They have a short travel distance, allowing for faster opening and closing, which is ideal for applications requiring quick responses.
Good Sealing: The minimal friction between the sealing surfaces ensures long-term sealing performance, extending the valve’s service life.
High Fluid Resistance: Due to the complex flow path, globe valves impose significant resistance on the fluid, requiring greater operating force during opening and closing, making the process less flexible.
Not Suitable for Complex Media: Globe valves are not ideal for media containing particles, viscous substances, or materials prone to coking, and their flow regulation capabilities are limited.
After understanding the structure and operating principles of both piston valves and globe valves, it is clear that they each have distinct performance characteristics and applications. The following comparison highlights key differences in sealing performance, speed, fluid resistance, adaptability, and application scenarios.
Piston valves offer a larger sealing area compared to globe valves, providing more reliable sealing, especially in high-temperature and high-pressure environments. While globe valves also have good sealing, they may face limitations when handling special media.
Globe valves have a faster opening and closing speed, making them suitable for situations requiring quick responses, while piston valves operate more slowly, making them better suited for stable conditions.
Globe valves introduce higher fluid resistance, requiring greater force to operate, especially during opening and closing. In contrast, piston valves provide smoother operation with less fluid resistance.
Piston valves are better suited for harsh environmental conditions, with wear-resistant sealing rings and large contact areas that extend their service life and reduce maintenance costs. Globe valves, with their more complex structure, are better for medium-duty fluid control applications.
Piston valves are ideal for high-temperature, high-pressure environments requiring excellent sealing, commonly found in petrochemical and chemical industries. Globe valves, on the other hand, are widely used in water treatment, heating systems, and applications requiring fast opening and closing.
When choosing a valve, it is essential to consider the specific operating conditions, characteristics of the fluid medium, and operational requirements. Piston valves, with their superior sealing and long service life, are best suited for applications with high sealing demands and complex media. In contrast, globe valves, with their simple structure and quick response, are ideal for general fluid control applications. Both valves have their strengths, and selecting the right one will enhance system efficiency and stability.
Cледующий: Уплотнение штока клапана: принципы, конструкции
Предыдущий: функциональность пружинного параллельного двойного задвижки
О нас
Продукция
Навигация
Our Contacts
Building 2, NO.59, Songshan Road, SND, Suzhou, China
