Swing vs. Lift Check Valves: What is the Difference?
Sep 04, 2024
On this page
Swing check valves and lift check valves are two types of check valves designed to prevent reverse flow in a system, each with its unique structural design and operating principles. Swing check valves are known for their simple and efficient swinging disc design, which ensures minimal pressure drop when fluid flows through, making them ideal for high-flow applications that require frequent opening and closing. In contrast, lift check valves control the flow of media through the lifting motion of the disc, offering higher sealing performance and resistance to water hammer, making them more suitable for systems with stringent sealing requirements. The choice and application of these check valves are directly related to the safety and operational efficiency of the system.
Swing check valves operate by using a hinged disc that swings open to allow fluid flow in the forward direction and closes to prevent reverse flow. This section will briefly analyze the structure, working principle, and advantages and disadvantages of swing check valves.
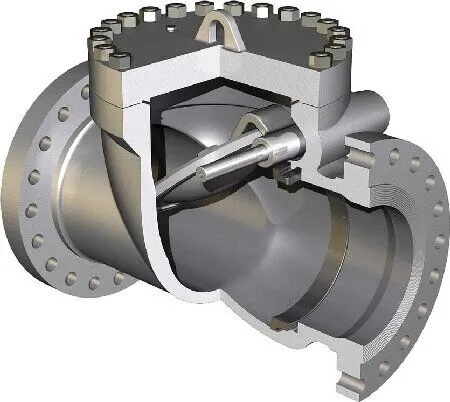
The key components of a swing check valve include a hinge mechanism and a disc that resembles a door. The disc freely rests on an inclined seat surface, and the hinge mechanism ensures that the disc reliably contacts the seat each time. The disc is designed to maintain full contact with the seat while rotating. Depending on performance requirements, the disc can be made entirely of metal or feature inserts of leather, rubber, or synthetic coverings to enhance sealing performance.
Opening Process: When the pump starts, the fluid enters through the inlet, overcoming the disc's weight and friction, pushing the disc open. At this point, the valve is open, and fluid flows smoothly to the outlet.
Closing Process: When the pump stops, the fluid begins to reverse flow, and the disc automatically closes due to the force of the spring and gravity, preventing backflow.
Advantages: Swing check valves offer minimal flow restriction when fully open, resulting in a relatively low-pressure drop. The design allows for a wide flow path, making them suitable for applications with high flow rates and frequent opening and closing.
Disadvantages: They generally provide lower sealing performance, making them unsuitable for applications requiring high sealing integrity. Additionally, swing check valves can only be installed horizontally.
Applications: These valves are ideal for installations with limited space, high operating pressure, and frequent opening and closing, such as pump stations and high-flow pipeline systems.
Lift check valves control fluid flow by the vertical movement of a disc. When the media flows in the forward direction, the disc is lifted, opening the valve; when reverse flow occurs, the disc falls back onto the seat, effectively cutting off flow and preventing backflow. This section will explore the structural characteristics and working mechanism of lift check valves.
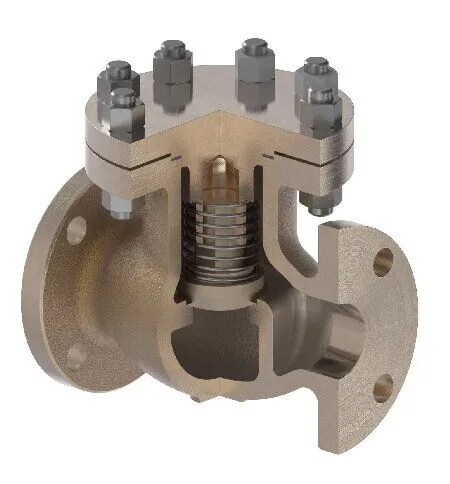

The disc of a lift check valve rests on the seat sealing surface within the valve body. The disc can freely lift and fall, sealing or opening the flow in conjunction with the seat's sealing surface. The disc can be entirely metal or embedded with rubber pads or rings to improve sealing performance. The design incorporates dual plates and two torsion springs to enable rapid disc closure, reducing water hammer pressure.
Opening Process: When the pump starts, the fluid enters through the inlet, overcoming the disc's weight, flow resistance, and the spring's resistance, pushing the disc upward to open the valve, allowing fluid to flow to the outlet.
Closing Process: When the pump stops, reverse flow occurs, outlet pressure drops, and the spring pushes the disc toward the seat, closing the valve and preventing backflow.
Advantages: Lift check valves provide high sealing performance, making them suitable for applications with stringent sealing requirements. The lifting disc design effectively reduces water hammer pressure.
Disadvantages: The opening and closing actions are slower, making them unsuitable for applications requiring rapid cycling. The fluid passage through the valve is relatively narrow, resulting in a higher pressure drop.
Applications: Lift check valves are suitable for installations with ample space, lower operating pressure, and high sealing requirements, such as large pipeline systems and applications where water hammer needs to be minimized. The vertical silent check valve, a variant of the lift check valve, is specifically designed for vertical installations.
When choosing between swing and lift check valves, it is essential to evaluate the specific requirements. Swing check valves are best suited for low-pressure drop, high-flow applications with frequent opening and closing, especially in systems with limited space and lower sealing demands. Lift check valves are preferable for systems that require high sealing integrity and resistance to water hammer, although their higher pressure drop and slower response time may be limiting factors in some applications. Therefore, selecting the appropriate valve depends on the working pressure, sealing requirements, installation space, and flow control priorities.
Swing Check Valves: These valves have a minimal pressure drop due to the unimpeded fluid path when fully open, making them suitable for high-flow and high-pressure applications.
Lift Check Valves: The narrower passage of lift check valves results in a higher pressure drop, making them more appropriate for low-flow applications.
Swing Check Valves: These valves are designed for horizontal installation.
Lift Check Valves: Primarily used in vertical installations, although horizontal installation models are available. The vertical silent check valve is designed specifically for vertical applications.
Swing Check Valves: Offer lower sealing performance but operate quickly, making them suitable for applications with frequent cycling.
Lift Check Valves: Provide high sealing performance but have a slower response, making them unsuitable for applications requiring rapid cycling.
Selecting the appropriate check valve is crucial in fluid control systems. Both swing check valves and lift check valves have distinct advantages and applications. Understanding their structural features, working principles, and respective strengths and weaknesses can help you make the best choice for different conditions, ensuring system stability and efficiency. Whether you prioritize the high flow and low-pressure drop of swing check valves or the superior sealing and water hammer resistance of lift check valves, the right choice will provide reliable assurance for your engineering projects.
Next: How to Choose Optimal Packing Material for Industrial Valves
Previous: Design and Advantages of Pneumatic Three-Way Ball Valves
About Us
Categories
Useful Links
Our Contacts
Building 2, NO.59, Songshan Road, SND, Suzhou, China
