API 607 Fire Safe Qualification Range for Valves
Jan 05, 2024
API 607 is a standard to defined fire test procedure for Quarter-turn valves and valves equipped with nonmetallic Seats. (For metal seated valves refer to API 6FA.)
This standard covers the requirements and method for evaluating the performance of valves when they are exposed to defined fire conditions.
In production facilities, valves are typically of a higher rating and the pressure source is not easily reduced when a fire is detected. Therefore, for all other valves, the test pressure during the burn is set at a higher value to better simulate the expected service conditions in these facilities.
And how to select a suitable valve to cover the valve list that is to be qualified?
Generally, when a valve is fire tested, the qualification can be extended to other valves according to Size, Pressure Rating, and Materials of Construction.
Size and pressure rating
1. A test valve may be used to qualify valves larger than the test valve but not exceeding twice the nominal size of the test valve. A size DN 200 or NPS 8 test valve qualifies for all larger sizes. lf the minimum size of a given range of valves is greater than DN 200 or NPS 8, then the minimum size of the range shall be tested to qualify all sizes.
2. DN 50 (NPS 2) valve may be used to qualify all smaller sizes of valves of the same type. If the maximum size of a given range of valves is smaller than DN 50 or NPS 2, then the maximum size of the range shall be tested to qualify all sizes.
3. A test valve may be used to qualify valves with higher class ratings but not exceeding twice the class rating of the test valve, except as shown in Tables 3 and 4.
4. A reduced-bore test valve may be used to qualify a smaller nominal-size full-bore valve when the components associated with the closure member, seat seals, and stem are identical in design and size. ln such a case the permissible average leakage rates are those applicable to the full-bore valve per Table 1 based on the valve NPS.
5. The type of valve body ends is not considered by this standard. However, the mass of the valve is determined in part by the body end type. For qualification to the present standard, and providing that all other qualification criteria have been met, valves with ends different from those of the test valve may also qualify, provided that their mass is greater than that of the test valve or their mass is not less than 75 % of that of the test valve.
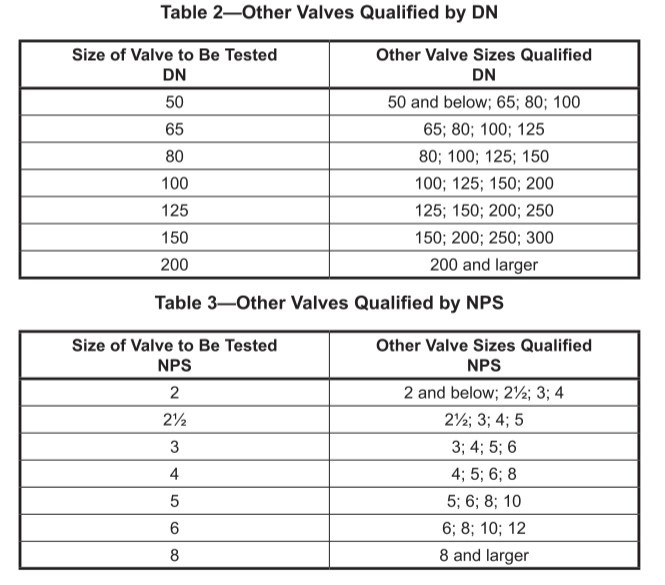
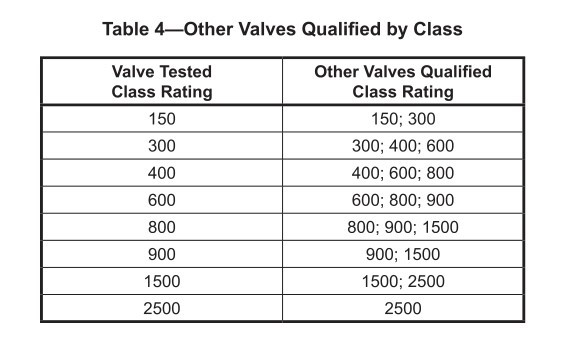
Materials of construction
Body & Bonnet
For product compliance certification or type-testing systems, the materials of construction of the pressure-retaining envelope of the valve shall be deemed to qualify other materials of construction within the generic classifications below, including but not limited to the listed material within each classification:
-ferritic, ASME B16.34 material
-austenitic, ASME B16.34 material
-duplex, ASME B16.34 material
-nickel alloys, ASME B16.34 material
Other critical material
lf a range of valves is covered by testing of ferritic test valves, then the type-testing coverage may be extended to cover austenitic, duplex, or nickel alloy materials by carrying out a further test on a single valve of each generic material and class range per Table 4. For product lines DN 50 (NPS 2) and below, the valve shall be of the maximum size of the product range. For those where the product line extends to larger sizes, the valve shall be equal to or greater than the median size in the ferritic testing. Other materials of construction of the pressure-retaining envelope of the valve require full testing of representative size and pressure ratings.
Alloy steel bolting (e.g. B7 or L7) used as part of the valve's pressure-retaining envelope may be used to qualify austenitic steel bolting but not vice versa.
Any change in the nominal composition of nonmetallic materials concerning the seat-to-closure member seal, seat-to-body seal, stem seal, or body joint seal requires a requalification, Filed PTFE, however, may qualify as non-filled PTFE and vice versa. Retest of a single valve equal to or greater than the median size of the previously tested product range is allowed for requalification for a change in a manufacturer of packing material.
Change of an elastomeric material type (e.g. FKM or HNBR) in the valve requires a retest of a single valve equal to or greater than the median size of the previously tested product range.
Bosseal Valves can supply ball valves, butterfly valves, and plug valves designed and tested according to API 607/API 6FA.
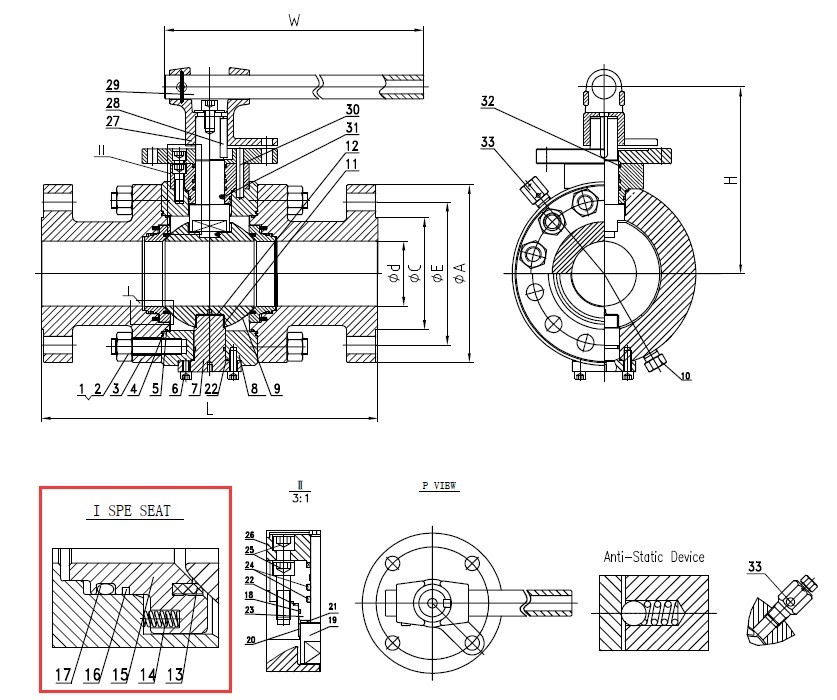
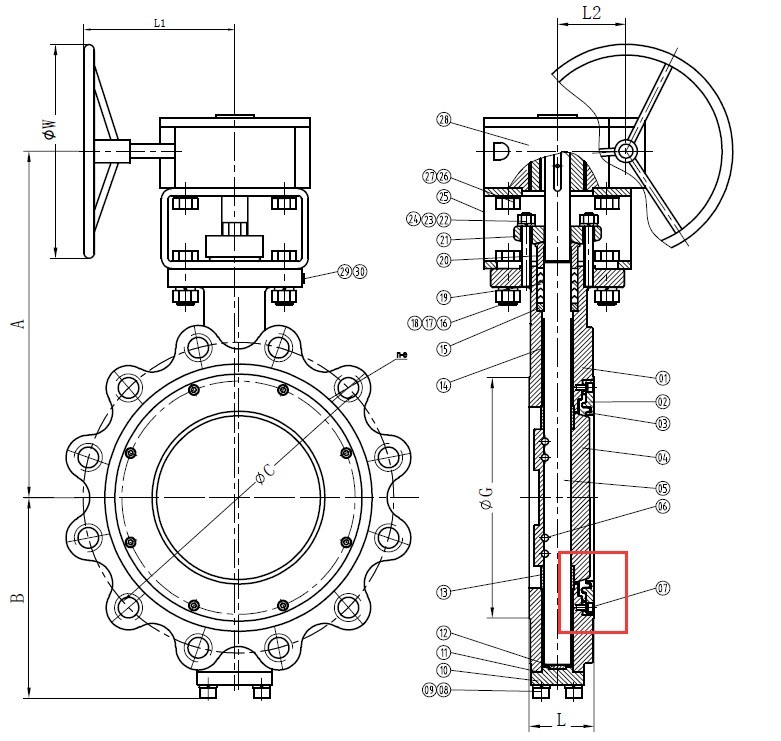

Bosseal Valve is a professional fire-safe designed and tested valve manufacturer, for any technical or commercial support please consider our teams at [email protected]
This standard covers the requirements and method for evaluating the performance of valves when they are exposed to defined fire conditions.
In production facilities, valves are typically of a higher rating and the pressure source is not easily reduced when a fire is detected. Therefore, for all other valves, the test pressure during the burn is set at a higher value to better simulate the expected service conditions in these facilities.
And how to select a suitable valve to cover the valve list that is to be qualified?
Generally, when a valve is fire tested, the qualification can be extended to other valves according to Size, Pressure Rating, and Materials of Construction.
Size and pressure rating
1. A test valve may be used to qualify valves larger than the test valve but not exceeding twice the nominal size of the test valve. A size DN 200 or NPS 8 test valve qualifies for all larger sizes. lf the minimum size of a given range of valves is greater than DN 200 or NPS 8, then the minimum size of the range shall be tested to qualify all sizes.
2. DN 50 (NPS 2) valve may be used to qualify all smaller sizes of valves of the same type. If the maximum size of a given range of valves is smaller than DN 50 or NPS 2, then the maximum size of the range shall be tested to qualify all sizes.
3. A test valve may be used to qualify valves with higher class ratings but not exceeding twice the class rating of the test valve, except as shown in Tables 3 and 4.
4. A reduced-bore test valve may be used to qualify a smaller nominal-size full-bore valve when the components associated with the closure member, seat seals, and stem are identical in design and size. ln such a case the permissible average leakage rates are those applicable to the full-bore valve per Table 1 based on the valve NPS.
5. The type of valve body ends is not considered by this standard. However, the mass of the valve is determined in part by the body end type. For qualification to the present standard, and providing that all other qualification criteria have been met, valves with ends different from those of the test valve may also qualify, provided that their mass is greater than that of the test valve or their mass is not less than 75 % of that of the test valve.


Materials of construction
Body & Bonnet
For product compliance certification or type-testing systems, the materials of construction of the pressure-retaining envelope of the valve shall be deemed to qualify other materials of construction within the generic classifications below, including but not limited to the listed material within each classification:
-ferritic, ASME B16.34 material
-austenitic, ASME B16.34 material
-duplex, ASME B16.34 material
-nickel alloys, ASME B16.34 material
Other critical material
lf a range of valves is covered by testing of ferritic test valves, then the type-testing coverage may be extended to cover austenitic, duplex, or nickel alloy materials by carrying out a further test on a single valve of each generic material and class range per Table 4. For product lines DN 50 (NPS 2) and below, the valve shall be of the maximum size of the product range. For those where the product line extends to larger sizes, the valve shall be equal to or greater than the median size in the ferritic testing. Other materials of construction of the pressure-retaining envelope of the valve require full testing of representative size and pressure ratings.
Alloy steel bolting (e.g. B7 or L7) used as part of the valve's pressure-retaining envelope may be used to qualify austenitic steel bolting but not vice versa.
Any change in the nominal composition of nonmetallic materials concerning the seat-to-closure member seal, seat-to-body seal, stem seal, or body joint seal requires a requalification, Filed PTFE, however, may qualify as non-filled PTFE and vice versa. Retest of a single valve equal to or greater than the median size of the previously tested product range is allowed for requalification for a change in a manufacturer of packing material.
Change of an elastomeric material type (e.g. FKM or HNBR) in the valve requires a retest of a single valve equal to or greater than the median size of the previously tested product range.
Bosseal Valves can supply ball valves, butterfly valves, and plug valves designed and tested according to API 607/API 6FA.

Ball Valve Fire Safe Seat

Butterfly Valve Fire Safe Seat


Bosseal Valve is a professional fire-safe designed and tested valve manufacturer, for any technical or commercial support please consider our teams at [email protected]
Next: TAT Qualification Range for valves - MESC SPE 77-300 (2022)
Previous: The Unrivaled Simplicity and Convenience of Three-Piece Ball Valves
About Us
Categories
Useful Links
Our Contacts
Building 2, NO.59, Songshan Road, SND, Suzhou, China
