Comparación de la válvula de compuerta de vástago ascendente y la válvula de compuerta de vástago ascendente oscura
Mar 01, 2024
In industrial applications, gate valves play a pivotal role as essential equipment for regulating fluid flow. The rising stem gate valves and non-rising stem gate valves are two common types, each with distinct characteristics influencing their operational mechanisms and suitability for different scenarios. Let's explore these gate valves further to understand their principles and applications.
Rising Stem Gate Valve: Structure and Characteristics
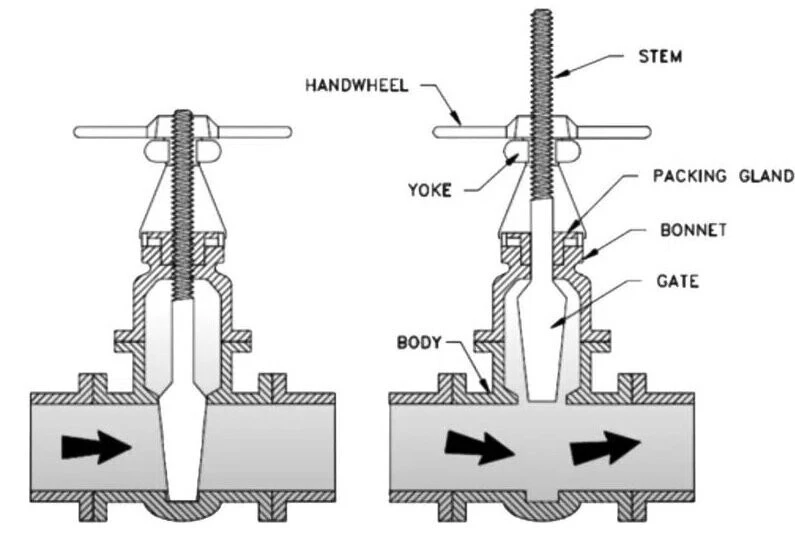
The rising stem gate valve is a prevalent type characterized by its mechanism of lifting and lowering the gate through the rotation of a handwheel connected to the stem's threads. This valve boasts advantages such as low fluid resistance, relatively effortless operation, and a straightforward structure suitable for controlling various types of media. However, the susceptibility of its sealing surfaces to erosion and abrasion poses challenges for maintenance and repair, often requiring considerable installation space.
Non-Rising Stem Gate Valve: Design and Features
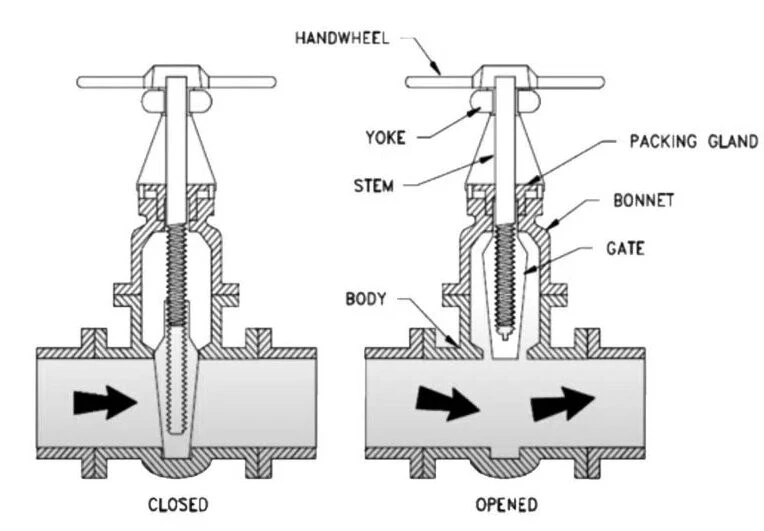
Also known as the non-rising stem or rotating stem gate valve, this type features a stem nut fixed on the gate, which, when rotated by a handwheel, causes the gate to ascend. Notable advantages of this valve include its compact structure and suitability for applications with large diameters or restricted installation spaces. Nevertheless, the inability to lubricate the stem threads and their susceptibility to media erosion present maintenance and repair challenges.
Major Differences Between the Two Gate Valves
The primary distinctions between these two valves lie in their structural design, operational mechanisms, and suitability for specific applications.
1. Appearance and Structure: The stem threads of a rising stem gate valve are visible, whereas those of a non-rising stem gate valve are concealed.
2. Operational Mechanism: The gate of a non-rising stem gate valve moves up and down through the stem's rotation at a fixed point, whereas in a rising stem gate valve, the gate moves up and down along with the stem, while the handwheel remains stationary.
3. Structural Features: The lifting screw of a non-rising stem gate valve only rotates without any vertical movement, with only a rod being exposed, lacking visible bonnets. On the other hand, the lifting screw of a rising stem gate valve is exposed, with the nut fixed on the handwheel, allowing the gate to ascend by rotating the screw, featuring a visible bonnet.
2. Operational Mechanism: The gate of a non-rising stem gate valve moves up and down through the stem's rotation at a fixed point, whereas in a rising stem gate valve, the gate moves up and down along with the stem, while the handwheel remains stationary.
3. Structural Features: The lifting screw of a non-rising stem gate valve only rotates without any vertical movement, with only a rod being exposed, lacking visible bonnets. On the other hand, the lifting screw of a rising stem gate valve is exposed, with the nut fixed on the handwheel, allowing the gate to ascend by rotating the screw, featuring a visible bonnet.
In summary, choosing between rising stem and non-rising stem gate valves hinges on specific needs and contexts. While rising stem valves offer straightforward operation but require more maintenance and space, non-rising stem valves are compact yet may pose maintenance challenges. Informed decision-making ensures equipment operates efficiently.
Siguiente: Solución de desafío de sellado de válvula de mariposa
Anterior: Tratamiento de fallas comunes de la válvula de bola en tuberías industriales
Sobre nosotros
Categorías
Enlaces útiles
Our Contacts
Building 2, NO.59, Songshan Road, SND, Suzhou, China